Research on tissues and body structures and biomaterials
Mechanical properties of osteoporotic bones
Project description:

Fig.1 Three-point bending of rat femur

Fig.2 Rat femoral neck bending
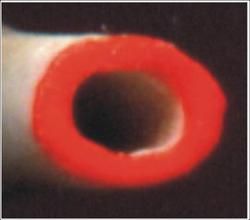
Fig.3a Bone cross-section image

Fig.3b Binary image of the bone cross-section
Osteoporosis is a disease that is characterized by retrogression of the mechanical resistance of the bones. This retrogression is a consequence of quantity and quality changes in the bone mass, and it leads to an increased risk of bone fractures. The decrease in sex hormone production after the menopause or andropause is the most frequent cause of osteoporosis; however in a high percentage of causes, osteoporosis is a secondary manifestation of other diseases or interpositions. Treatment for osteoporosis must therefore correspond with the causative agent and with the state of the patient.
In the Czech Republic osteoporosis afflicts 15% of men and 33% of women over the age of 50, and 39% of men and 47% of women over the age of 70. Fractures of the vertebra and hip are the most serious hazards of osteoporosis that significantly reduce life quality and longevity. There are over 17000 cases annually of a typical fracture of the proximal femur in the Czech Republic.
The following methods for determining bone properties are used in medicine: ultrasound transmission velocity (UTV) and bone mineral density (BMD). However, there is increasing demand for the evaluation of more parameters, especially in the area of mechanical stress distribution in the bone, so that the Laboratory of Biomechanics has started to study the mechanical resistance of bones to various types of loading. The three-point bending test (Figure 1), femoral neck bending (Figure 2) and nanoindentation is used for bone testing. The main benefit is that the mechanical properties of healthy and treated bones can be compared, and these findings can be confronted with medical tests of osteoporotic bones (e.g. UTV and BMD).
In Laboratory of Biomechanics the biomechanical testing system MTS Mini Bionix is used for the three-point bending test and femoral neck bending and is placed in the accredited Mechanical Testing Laboratory. The program, written for the test control in TestWare software, controls crosshead speed and measures important quantities such as load, deflection and time. The recorded values together with sectional modulus of bone are necessary for the calculation of several biomechanical parameters of bone that can be used to characterize the bone integrity, such as the bending strength, flexural rigidity, work to failure, elastic modulus, etc.
For sectional modulus determination the methodology was developed, in that the bone cross-section is squared up, marked by the coloured felt-tip and scanned at resolution 1200x1200 dpi (Figure 3a). The pictures obtained from scanner are converted as the binary picture into the program that is created in Matlab. (Figure 3b) This program calculates every important dimensions of the bone and sectional modulus of bone Womin.
In the last years we realized the research of the effect of the select substances on the biological and mechanical characteristics of osteoporotic bones. Together with doctors from the First Faculty of Medicine on Charles University we targeted the male population and we tested the effect of Nicotine and Alcohol on the biological and mechanical characteristics of osteoporotic bones from male rat.
The next work will consist in the development of aforesaid testing methods and first of all in the research of the effect of other drugs and hormones on the mechanical properties of rat femurs.
Josef Šepitka Ph.D. ; doc. Ing. Radek Sedláček, Ph.D. ; Ing. Pavel Růžička, Ph.D.Resesrchers:
III. Internal clinic 1st. Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague